Extra-terrestrial oceans, extra-terrestrial habitats, and extra-terrestrial life
I have been studying the surface tectonics, interior structure, chemical composition, and their evolution of the icy satellites, which belong to giant planets using computer simulation and observational data analyses, in particular.
In addition, interior evolution of terrestrial Moon and its evolution is also my interest in a viewpoint of comparative understandings between icy and rocky bodies.
Ultimately, I'd like to explain how planets and satellites have evolved to the current states and how the planets and the satellites diverged on their evolution. And what is condition for emerging an extra-terrestrial life.
I participated in the exploration mission project, SELENE/KAGUYA, Japanese lunar mission from 2007 to 2009. Now I'm a member of LIDAR (Laser Altimeter) team on the HAYABUSA-2 mission which has been launched in December 2014 to C-type asteroid "1999JU3", and GALA (Ganymede Laser Altimeter) team on the JUICE (JUpiter ICy moons Explorer) mission which will be launched to the Jupiter system in 2022.
As an ELSI research scientist, I particularly focuses on the habitability of the icy satellites and the exo-icy planets/moons to provide some important constraints on the thermal/structural evolution and chemical composition of the subsurface ocean if exists, which are essentially important to understand a different style of biosphere from the Earth.
Environment of icy moon: origin and evolution
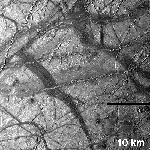
Most of the satellites in the system of gas giants have an ice as one of the main component, called "icy satellites". On many of the icy satellites, various types of the tectonic features can be seen. We investigate the stress sources for the formation of these features, i.e., tensile cracks (lineated ridges, band-shaped features). Especially, we pay attention to the interaction between the internal thermal history and surface tectonics.
Moreover, we focus on the thermal activities within the icy shell affecting the formation of chaotic terrain on Europa, methane migration on Titan, and geysers on Triton, etc [imaged by NASA].
- Thermal and structural history

Some of icy satellites (Europa, Callisto, Ganymede, Enceladus, Titan, Triton,,,) are implied that the internal liquid water ocean exists under the icy surface. We perform the numerical simulation for the structural evolution, especially focus on the existence of internal ocean and growth of icy shell. Growth speed of the icy shell (solidification rate of the internal ocean) and accompanying volume change is significant to discuss the stress source of icy shell [imaged by NASA].
- Dynamo activity in the moon's core
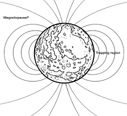
Galileo spacecraft has discovered the strong intrinsic magnetic field on Ganymede. This field is considered to mainly originate by self-excited dynamo activity in the metallic core. The driving of dynamo depends critically on the thermal state and internal structure. However, inferred structure based on gravity data has large uncertainty and this makes the possibility of dynamo activity unclear; variation of the core size and the composition greatly change the heat capacity and hence, it alters the cooling history of the core. We perform the numerical simulation on the thermal history of the core and try to constrain the size and composition of the metallic core based on the condition of driving a dynamo activity [imaged by NASA].
- Astrobiology

Ice covered satellites and planets are common in the solar system. Many of large icy satellites indicating the existence of a liquid water layer are strong candidate for extraterrestrial life. Jovian satellite Europa is one of the most significant example which has implied by magnetic observations and geomorphological interpretations. We focus on the hydrothermal activity in the region between internal liquid ocean and solid rocky mantle and evaluate the thermal and chemical affects.
Also, we investigate chemical evolution in the icy moon's environment. In particular, we perform thermodynamic calculations (e.g., free energy) for polymerization of amino acids and other building bloks of life.



